To solve the quadratic functions we need to know the required concepts:
The quadratic formula is used to find the roots of a quadratic equation given in the standard form \( ax^2 + bx + c = 0 \). The formula is:
\[
x = \frac{-b \pm \sqrt{b^2 – 4ac}}{2a}
\]
Vertex of a Quadratic Function
The vertex \((h, k)\) of a quadratic function \( f(x) = ax^2 + bx + c \) can be found using the formulas:
\[
h = -\frac{b}{2a}
\]
Once \( h \) is found, substitute it back into the function to find \( k \):
\[
k = f(h) = a\left(-\frac{b}{2a}\right)^2 + b\left(-\frac{b}{2a}\right) + c
\]
Simplifying the expression for \( k \), we have:
\[
k = \frac{4ac – b^2}{4a}
\]
Hence, the vertex is \(\left(-\frac{b}{2a}, \frac{4ac – b^2}{4a}\right)\).
Axis of Symmetry
The axis of symmetry of the quadratic function \( f(x) = ax^2 + bx + c \) is the vertical line that passes through the vertex. It is given by the equation:
\[
x = -\frac{b}{2a}
\]
This line divides the parabola into two mirror-image halves.
Maximum and Minimum
The quadratic function \( f(x) = ax^2 + bx + c \) can have either a maximum or a minimum value depending on the coefficient \( a \).
Minimum Value
– If \( a > 0 \), the parabola opens upwards, and the function has a **minimum** value at the vertex.
Maximum Value
– If \( a < 0 \), the parabola opens downwards, and the function has a **maximum** value at the vertex.
Vertex and Extrema
The vertex of the quadratic function, where the maximum or minimum occurs, is given by:
\[
h = -\frac{b}{2a}
\]
The corresponding function value at the vertex is:
\[
k = f(h) = a\left(-\frac{b}{2a}\right)^2 + b\left(-\frac{b}{2a}\right) + c = \frac{4ac – b^2}{4a}
\]
Thus, the vertex is \(\left(-\frac{b}{2a}, \frac{4ac – b^2}{4a}\right)\).
– **Minimum Value**: \(\frac{4ac – b^2}{4a}\) when \( a > 0 \).
– **Maximum Value**: \(\frac{4ac – b^2}{4a}\) when \( a < 0 \).
Parabola Behavior
For the quadratic function \( f(x) = ax^2 + bx + c \),
If a>o, f(x)→ ∞ when x→ ∞ or x→-∞.
If a<0, f(x) → -∞ when x→∞ or x→ -∞.
Intervals of Increase or Decrease
A quadratic function is increasing if the function slopes upwards from left to right along the x-axis.
A quadratic function is decreasing if the function slopes downwards from left to right along the x-axis.
Example 1. Given the graph of f(x)= \(-4x^2+2x+6\) below, determine the following:
a) Find the intervals of increase and decrease.
b) Identify the domain and range.
c) Determine the end behavior of the function.
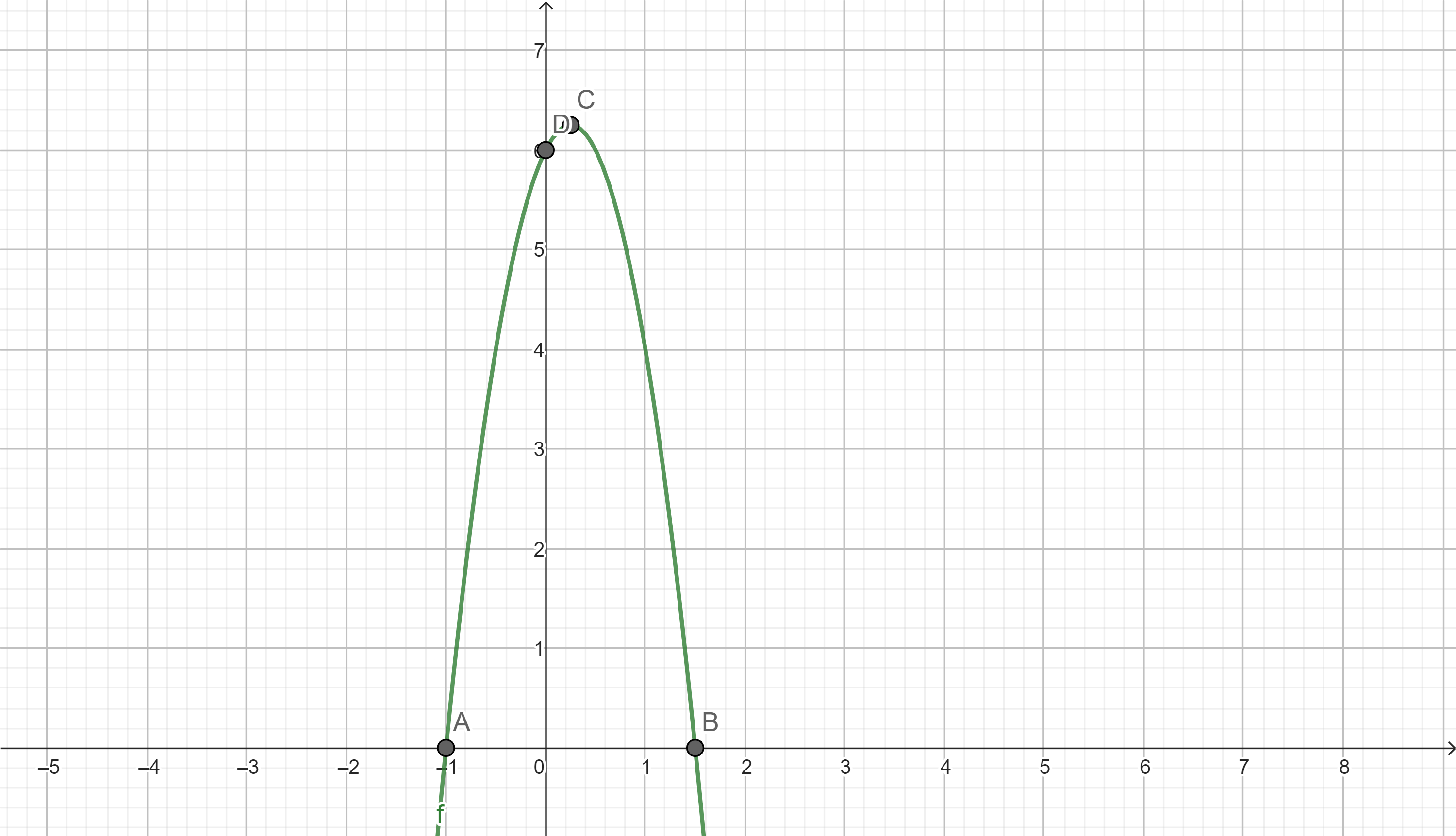
Answer: The function is given as: f(x)= \(-4x^2+2x+6\)
Here, a= -4, b= 2 and c= 6.
Roots of f(x) = \(-4x^2+2x+6\) are (-1,0) and ( 1.5,0) (Points A &B in graph).
y- intercept => (0,6) (Point D in the graph).
a) At first, we have to calculate the vertex of the function to determine the intervals of increase and decrease.
(h,k) = \(\left(-\frac{b}{2a}, \frac{4ac – b^2}{4a}\right)\).
Thus, (h,k)= \(\left(-\frac{2}{2(-4)}, \frac{4*(-4)*6 – 2^2}{4(-4)}\right)\).
= \(\left(-\frac{-2}{8}, \frac{-96-4}{-16}\right)\).
= \(\left(\frac{1}{4}, \frac{-100}{-16}\right)\).
= \(\left(\frac{1}{4}, \frac{25}{4}\right)\).
= (0.25, 6.25) (Point C in the graph).
Now, we can calculate the intervals of increase and decrease.
We know that a quadratic function is decreasing if the function slopes downwards from left to right along the x- axis and increasing if the function slopes upwards from left to right along the x- axis.
Here, from the graph , the function f(x) is increasing from (-∞, 0.25) and decreasing from (0.25,∞).
b) Domain and Range of the function.
According to the graph, both the left and right ends of the function continue downward indefinitely. Therefore, the domain of the function for all the real numbers, -∞<x<∞, or (-∞,∞).
From the graph, the maximum y- value occurs at 6.25 and the graph continues downwards indefinitely. So, the range of the function for all real numbers, -∞<y≤ 6.25, or (-∞, 6.25].
c) End Behavior of the function.
Left End: As the value of x approaches -∞, f(x) also approaches -∞.
Right End: As the value of x approaches ∞, f(x) approaches -∞.
Hence, the end behavior: f(x)→-∞, as x→-∞
and f(x)→-∞, as x→∞.
Example 2. Determine the number of real solutions in the function
f(x)= \(- 2 x^2 + 5x +4 \)
using the Discriminant. If real solutions exist, use the quadratic formula to find the solutions. Then do the following:
a) Identify the y- intercept.
b) Identify the vertex and state whether it is a minimum or maximum.
c) Identify the axis of symmetry.
d) Draw the function in the coordinate plane and determine the domain, range and end behavior.
Answer: First determine that if the quadratic has any real solutions .
The function
f(x)= \(- 2 x^2 + 5x +4 \)
is already in standard form , we know that a= -2,b= 5and c= 4.
Discriminant, D= \( b^2-4ac = 5^2 – 4*(-2)*4 = 25 -(-32) = 25+ 32 = 57\)
The Discriminant is positive, so the quadratic has two real solutions. Lets find them by using the Quadratic Formula:
\[
x = \frac{-b \pm \sqrt{b^2 – 4ac}}{2a}
\]
\[
x = \frac{-5 \pm \sqrt{5^2 – 4*(-2)*4}}{2(-2)}
\]
\[
x = \frac{-5 \pm \sqrt{25 – (-32)}}{-4)}
\]
\[
x = \frac{-5 \pm \sqrt{25+32}}{-4}
\]
\[
x = \frac{-5 \pm \sqrt{57}}{-4}
\]
Therefore,
\[
x = \frac{-5 + \sqrt{57}}{-4}
\]
&
\[
x = \frac{-5 – \sqrt{57}}{-4}
\]
So, x=-0.64 and 3.14
Thus, the x- intercepts of f(x)= \(- 2 x^2 + 5x +4 \) occurs at (-0.64,0) and (3.14,0).
Now, find the y- intercept by setting x=0 and solving for f(x).
f(x)= \(- 2 x^2 + 5x +4 \)
f(0)= \(- 2 *0^2 + 5*0 +4 \)
= \(0+4\)
=4.
So, the y- intercept occurs at (0,4).
Next find the Vertex ,(h,k), of f(x)= \(- 2 x^2 + 5x +4 \)
Given that a=-2, b=5 and c=4.
Vertex
The \( x \)-coordinate of the vertex is given by:
\[
h = -\frac{b}{2a} = -\frac{5}{2(-2)} = \frac{5}{4}
\]
Substitute \( h \) back into the function to find the \( y \)-coordinate (\( k \)) of the vertex:
\[
k = f\left(\frac{5}{4}\right) = -2\left(\frac{5}{4}\right)^2 + 5\left(\frac{5}{4}\right) + 4
\]
\[
k = -2 \cdot \frac{25}{16} + \frac{25}{4} + 4
\]
\[
k = -\frac{50}{16} + \frac{100}{16} + \frac{64}{16} = \frac{114}{16} = \frac{57}{8}
\]
Thus, the vertex is \(\left(\frac{5}{4}, \frac{57}{8}\right)\) or (h.k)= (1.25, 7.13).
Axis of Symmetry
The axis of symmetry is the vertical line passing through the vertex:
\[
x = \frac{5}{4}
\]
x= 1.25
Graph
Now, let’s plot the graph of the function.

From the graph:
Domain
Since, both the left and right ends of the function continue downward indefinitely, so the domain is all real numbers, -∞ <x<∞,or (-∞,∞).
Range
Tha maximum y- value occurs at 7.125 and the graph continues downwards indefinitely. SO, teh range is all real numbers, -∞ <y≤7.125, or (-∞<y≤7.125].
End Behavior
Left end: As the value of x approaches -∞ the value of f(x) also approaches -∞.
Right end: As the value of x approaches ∞, the value of f(x) approaches -∞.
f(x) → -∞ , as x →-∞
f(x) → -∞, as x →∞.



Leave a Reply